- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact of Hyperoxia and Hypocapnia on Neurological Outcomes in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Retrospective Study
Read this article at
Abstract
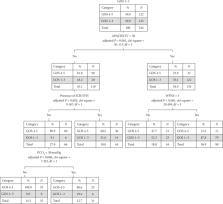
In recent decades, there is increasing evidence suggesting that hyperoxia and hypocapnia are associated with poor outcomes in critically ill patients with cardiac arrest or traumatic brain injury. Yet, the impact of hyperoxia and hypocapnia on neurological outcome in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has not been well studied. In the present study, we evaluated the impact of hyperoxia and hypocapnia on neurological outcomes in patients with aneurysmal SAH (aSAH). Patients with aSAH who were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of a tertiary hospital in Hong Kong between January 2011 and December 2016 were retrospectively recruited. Patients' demographics, comorbidities, radiological findings, clinical grades of SAH, PO 2, and PCO 2 within 24 hours of ICU admission, and Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) at 3 months after admission were recorded. Patients with a GOS score of 3 or less were considered having poor neurological outcomes. Among the 244 patients with aSAH, 122 of them (50%) had poor neurological outcomes at 3 months. Early hyperoxia (PO 2 > 200 mmHg) and hypercapnia (PCO 2 > 45 mmHg) were more common among patients with poor neurological outcomes. Logistic regression analysis indicated that hyperoxia independently predicted poor neurological outcomes (OR 3.788, 95% CI 1.131–12.690, P=0.031). Classification tree analysis revealed that hypocapnia was associated with poor neurological outcomes in patients who were less critically ill (APACHE < 50) and without concomitant intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) or intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) (adjusted P=0.006, χ 2 = 7.452). These findings suggested that hyperoxia and hypocapnia may be associated with poor neurological outcomes in patients with aSAH.
Related collections
Most cited references22
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Incidence of subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic review with emphasis on region, age, gender and time trends.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Association between arterial hyperoxia following resuscitation from cardiac arrest and in-hospital mortality.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found