- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Development of Validated Methods and Quantification of Curcuminoids and Curcumin Metabolites and Their Pharmacokinetic Study of Oral Administration of Complete Natural Turmeric Formulation (Cureit™) in Human Plasma via UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF-MS Spectrometry
Read this article at
Abstract
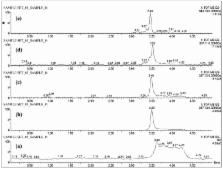
Specific and sensitive ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight-mass spectroscopy (UPLC-QTOF-MS) methods have been developed for the determination of curcuminoids and curcumin metabolites in human blood plasma. The UPLC-QTOF-MS method used a binary solvent delivery system and the chromatographic separation was performed on a C-18 (2.1 × 50 mm; 1.7 µm) column. Mass spectra were obtained on a Waters Xevo G2S Q-TOF mass spectrometer. The developed methods to characterize the pharmacokinetics of curcuminoids and curcumin metabolites in human blood plasma after an oral administration of bioavailable curcumin—Cureit™—were validated. It was found that the complete turmeric matrix enhances the concentration of tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), hexahydrocurcumin (HHC), octahydrocurcumin (OHC), curcumin- O-glucuronide (COG) and curcumin- O-sulfate (COS) in the blood plasma once the product is administrated.
Related collections
Most cited references17
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The revision of the Declaration of Helsinki: past, present and future.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Curcumin is a potent DNA hypomethylation agent.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Enhancement of curcumin oral absorption and pharmacokinetics of curcuminoids and curcumin metabolites in mice.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.