- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Six‐Stage Workflow for Robust Application of Systems Pharmacology
Read this article at
Abstract
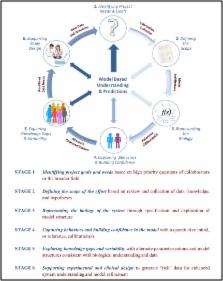
Quantitative and systems pharmacology (QSP) is increasingly being applied in pharmaceutical research and development. One factor critical to the ultimate success of QSP is the establishment of commonly accepted language, technical criteria, and workflows. We propose an integrated workflow that bridges conceptual objectives with underlying technical detail to support the execution, communication, and evaluation of QSP projects.
Related collections
Most cited references85
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Causal protein-signaling networks derived from multiparameter single-cell data.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Systems Biology Graphical Notation.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.