- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical responses to ERK inhibition in BRAF V600E-mutant colorectal cancer predicted using a computational model
Read this article at
Abstract
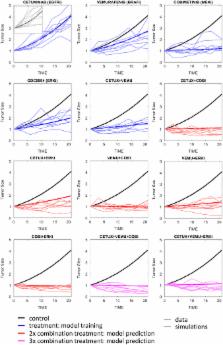
Approximately 10% of colorectal cancers harbor BRAF V600E mutations, which constitutively activate the MAPK signaling pathway. We sought to determine whether ERK inhibitor (GDC-0994)-containing regimens may be of clinical benefit to these patients based on data from in vitro (cell line) and in vivo (cell- and patient-derived xenograft) studies of cetuximab (EGFR), vemurafenib (BRAF), cobimetinib (MEK), and GDC-0994 (ERK) combinations. Preclinical data was used to develop a mechanism-based computational model linking cell surface receptor (EGFR) activation, the MAPK signaling pathway, and tumor growth. Clinical predictions of anti-tumor activity were enabled by the use of tumor response data from three Phase 1 clinical trials testing combinations of EGFR, BRAF, and MEK inhibitors. Simulated responses to GDC-0994 monotherapy (overall response rate = 17%) accurately predicted results from a Phase 1 clinical trial regarding the number of responding patients (2/18) and the distribution of tumor size changes (“waterfall plot”). Prospective simulations were then used to evaluate potential drug combinations and predictive biomarkers for increasing responsiveness to MEK/ERK inhibitors in these patients.
Systems pharmacology:Predicting efficacy of novel anti-cancer drugs in colorectal cancer
While cancer drug development relies on experimental tumor models for testing, results observed in these systems often fail to translate clinically. Kirouac et al. demonstrate how computational systems modelling can help bridge this divide. Focusing on a class of colorectal cancers with poor prognosis (those with a mutant form of the BRAF oncogene) they develop a mathematical model linking drug exposure, via cellular signal transduction, to tumor growth. By triangulating experimental data from multiple cell lines and mouse models, with results from three clinical trials of related drugs, the model accurately predicted tumor shrinkage observed in a first-in-human study of GDC-0994, an ERK inhibitor. Simulations were then used to explore strategies for increasing the activity of this class of drugs (MAPK pathway inhibitors) via combinations, alternate dosing regimens, and predictive biomarkers to guide future clinical studies. Extended to other cancer types and drugs, the approach could streamline early clinical development.
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Discovery of a novel ERK inhibitor with activity in models of acquired resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Computational modeling of the dynamics of the MAP kinase cascade activated by surface and internalized EGF receptors.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.