- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Importance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives
Abstract
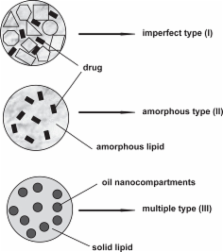
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) have been reported to be an alternative system to emulsions, liposomes, microparticles and their polymeric counterparts for various application routes since the early 1990s due to their advantages. Various research groups have also increasingly focused on improving their stability in body fluids after administration by coating of particles with hydrophilic molecules such as poly(ethylene)glycol (PEG) derivatives. Altering surface characteristics by coating SLN with hydrophilic molecules improves plasma stability and biodistribution, and subsequent bioavailability of drugs entrapped. Their storage stability is also increased. This paper basicly reviews types of SLN, principles of drug loading and models of drug incorporation. The influence of PEG coating on particle size and surface characteristics is discussed followed by alteration in pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of drugs in order to target the site of action via SLN. The future direction of research and clinical implications of SLN is also considered.
Most cited references161
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found