- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
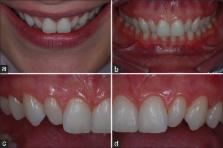
Providing a harmonious smile with laminate veneers for a patient with peg-shaped lateral incisors
Read this article at
Abstract
The most common discrepancy concerning tooth size is the presence of peg-shaped lateral incisors, which can cause teeth with reduced size, anterior diastema, and consequently an unpleasant smile. The development of the adhesive dentistry and ceramic veneers allowed all ceramic-bonded restorations to become an esthetic and functional approach to reestablish the smile harmony. The purpose of this clinical report is to describe a conservative treatment approach to recover an esthetic disharmony caused by bilateral peg-shaped lateral incisors. A 30-year-old female patient was seeking treatment to solve an esthetic disharmony of her smile. Lithium disilicate veneers were planned and build-up with the help of diagnostic models, wax-up, mock-up, and silicone guides, to restore the morphology, size, function, and esthetic of upper lateral incisors and smile. The lithium disilicate veneers were able to provide the harmonization of the patient's smile, recovering the teeth size, shape, and anatomic characteristics.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A critical review of the durability of adhesion to tooth tissue: methods and results.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The bleaching of teeth: a review of the literature.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found