- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Khat chewing and its associated factors among pregnant women in Chiro district, eastern Ethiopia: a community-based study
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Despite its deleterious consequences, khat chewing is escalating worldwide. However, there is a lack of evidence about the extent of khat chewing among pregnant women in Ethiopia, particularly in the current study area. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the prevalence of current khat chewing and its associated factors among pregnant women in Chiro district, eastern Ethiopia.
Methods
This community-based cross-sectional study was conducted in Chiro district from November 1 to 30, 2022 G.C. Study participants were selected using the systematic random sampling technique. An interview-administered structured questionnaire was used to collect data through a house-to-house survey. The data were entered into EpiData version 3.1 and analyzed in STATA 14 software. Characteristics of study participants were summarized using descriptive analysis, and binary logistic regression was used to identify determinants of khat chewing.
Results
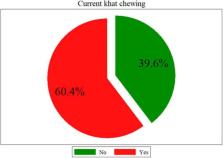
A total of 409 pregnant women participated in this study, with a response rate of 99%. The overall prevalence of khat chewing was 60.4% (95% CI: 55.5%, 65.2%). Religion (AOR: 2.08; 95% CI: 1.13, 3.82), khat cultivation (AOR: 0.43; 95% CI: 0.25, 0.77), partner khat use (AOR: 5.54; 95% CI: 3.11, 9.88), pre-pregnancy khat use (AOR: 9.95; 95% CI: 5.55, 17.81), antenatal care (ANC) visit (AOR: 2.71; 95% CI: 1.41, 5.21), and mental distress (AOR: 4.89; 95% CI: 2.38, 10.02) were significantly associated with current khat chewing.
Conclusion
The majority of pregnant women in the study area practice khat chewing. Thus, accessible and comprehensive pre-conception and pre-natal care incorporating the prevention and management of antenatal khat chewing is crucial to overcome this problem. Provision of mental healthcare involving partners of pregnant women is also important to reduce the extent and impacts of khat chewing during pregnancy. Further longitudinal studies triangulated with qualitative designs are recommended.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Detecting perinatal common mental disorders in Ethiopia: validation of the self-reporting questionnaire and Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Khat (Catha edulis)-an updated review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found