- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A convolutional neural network for estimating synaptic connectivity from spike trains
Read this article at
Abstract
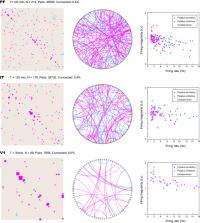
The recent increase in reliable, simultaneous high channel count extracellular recordings is exciting for physiologists and theoreticians because it offers the possibility of reconstructing the underlying neuronal circuits. We recently presented a method of inferring this circuit connectivity from neuronal spike trains by applying the generalized linear model to cross-correlograms. Although the algorithm can do a good job of circuit reconstruction, the parameters need to be carefully tuned for each individual dataset. Here we present another method using a Convolutional Neural Network for Estimating synaptic Connectivity from spike trains. After adaptation to huge amounts of simulated data, this method robustly captures the specific feature of monosynaptic impact in a noisy cross-correlogram. There are no user-adjustable parameters. With this new method, we have constructed diagrams of neuronal circuits recorded in several cortical areas of monkeys.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Deep learning.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found