- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association of socio-demographic factors with clinical outcome among hospitalized patients in first and second waves of COVID-19 pandemic: Study from the developing world
Read this article at
A BSTRACT
Background:
Recent disease resurgence in China indicates that corona virus infectious disease is still a pertinent public health problem. We stand at a juncture where we are still unsure about the initial dilemmas regarding its birth, therapies, and the emerging novel strains. Medical literature has focused on the clinical, laboratory, radiological, and therapeutic aspects of disease management. There is paucity of literature on the association between socio-demographic variables on disease severity and clinical outcome.
Materials and Methods:
This retrospective observational study analyzing the socio-demographic variables was performed at a dedicated COVID care center in western Maharashtra, India. Electronic records of all individuals who were admitted to this hospital from July 29 2020, to June 14, 2021, and diagnosed COVID-19 positive by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) were identified after due institutional ethical clearance. Patients admitted from July 29, 2020, to February 27, 2021, were categorized as patients presenting during the ‘first wave of viral pandemic’. Those admitted from March 01, 2021, to June 14, 2021, have been included as patients admitted during ‘second wave of viral pandemic’. The following outcome parameters were collected (presenting symptoms, duration of symptoms before the individual presented for diagnostic RT-PCR, total duration of symptoms, severity of disease at onset, duration of hospital stay, the final outcome (discharge/death) and Charlson’s comorbidity index). The linear regression model was used to establish association between socio-demographic factors and disease severity at onset (mild/moderate/severe/critical).
Results:
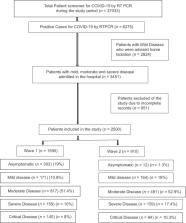
A total of 37033 patients were screened, and the positivity rate with RT-PCR was 16.99% ( n = 6275) during the study period. Out of which 45% ( n = 2824) of the patients had mild disease requiring home isolation and the remaining 55% of patients required admission. 1590 patients from the first wave and 910 from the second wave of COVID-19 were hospitalized and included in the study after exclusion. The mean age of patients in first wave was 49 years and that in second wave was 54 years with 77.6% and 70.6% males in two waves, respectively. The burden of critical cases was higher in second wave as computed to first wave (10% vs 8%). The second wave had more outreach in the rural population as compared to second one (17.8% vs 12.2%). The mean duration from the onset of symptoms to hospitalization was 03 and 04 days, respectively, in two waves. Mortality associated in two waves was 11.9% and 24%, respectively ( P < 0.05). Higher Charlson’s comorbidity index was associated with higher mortality, and the cumulative survival from urban area was more as compared to the rural population (log rank - 9.148, P = 0.0002).
Conclusion:
The second COVID-19 wave had significantly higher case mortality. It affected elderly patients and those with rural background. The factors associated with higher mortality during COVID-19 pandemic were rural background, higher Charlson’s comorbidity index and late presentation to the hospital. Ongoing vaccine campaigns, thus, should focus on rural areas and individuals with comorbidities especially in developing and least developed countries.
Related collections
Most cited references22
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mucormycosis in COVID-19: A systematic review of cases reported worldwide and in India

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found