- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Predictors of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis among High-Risk Population Diagnosed under National Program Conditions in the Littoral Region, Cameroon
Read this article at
Abstract
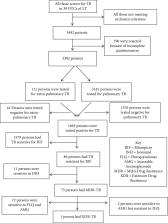
Multiple drug resistance TB (MDR-TB) has greatly jeopardized the effective control of tuberculosis in Africa. This study is aimed at determining the incidence and predictors of drug resistant-TB amongst bacteriologically diagnosed cases in the Littoral region of Cameroon. This was a descriptive cross-sectional survey conducted from January 2016 to December 2017. A total of 1665 participants were enrolled from 32 diagnostic and treatment centers (DTCs) in the Littoral region. Demographic, clinical, socioeconomic, and behavioral data were obtained using a pretested structured questionnaire. Drug susceptibility testing was performed using Gene Xpert MTB/RIF assay and line probe assay (LPA). Consent was obtained from participant/guidance. Data analysis was carried with SPSS version 21. Univariate and multiple logistic regression was performed at 5% significance level. The incidence of rifampicin and MDR-TB was 86 (5.2%) and 75 (4.5%), respectively. More (11.3%) cases of drug resistance were diagnosed in 2016 compared to 2017 (3.7%). Eleven (0.7%) were resistant to rifampicin only. A total of 19 (4.4%) cases of rifampicin resistance were detected from newly diagnosed cases and 67 (5.4%) from previously retreated cases. Pre-XDR-TB was detected in 2 (2.7%) of the MDR-TB cases amongst whom 1 (1.3%) was extensive drug resistance TB (XDR-TB). Age greater than 60 years old (OR = 4.98, p = 0.047), being married (OR = 1.91, p = 0.006), being currently incarcerated (OR = 1.74, p = 0.027), and having contact with known TB cases (OR = 1.88, p = 0.007) were associated to MDR-TB in a univariate analysis. This study highlights the declining rates of TB drug resistance in the region over the years probably due to the introduction of Gene Xpert that results in early detection of RR-TB. It also shows that age greater than 60 years, being married, and incarcerated are predictors of drug resistant-TB, while the year of patient enrolment and previous exposure to TB treatment were independent predictors of drug resistance in the Littoral region of Cameroon.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global lung health: the colliding epidemics of tuberculosis, tobacco smoking, HIV and COPD.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Poor lung ultrasound score in shock patients admitted to the ICU is associated with worse outcome

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Molecular Diagnosis of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis; A Literature Review
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
