- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficacy of Superselective Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization Using Guidance Software for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Three Lesions Smaller Than 3 cm
Read this article at
Abstract
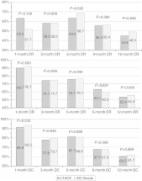
The indication of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) has advanced to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage A when surgical resection (SR), thermal ablation, and bridging to transplantation are contraindicated; however, TACE for small HCC is frequently difficult and ineffective because of less hypervascularity and the presence of tumor portions receiving a dual blood supply. Here, we report outcomes of superselective conventional TACE (cTACE) for 259 patients with HCCs within three lesions smaller than 3 cm using guidance software. Automated tumor feeder detection (AFD) functionality was applied to identify tumor feeders on cone-beam computed tomography during hepatic arteriography (CBCTHA) data. When it failed, the feeder was identified by manual feeder detection functionality and/or selective angiography and CBCTHA. Regarding the technical success in 382 tumors (mean diameter, 17.2 ± 5.9 mm), 310 (81.2%) were completely embolized with a safety margin (5 mm wide for HCC ≤25 mm and 10 mm wide for HCC >25 mm). In 61 (16.0%), the entire tumor was embolized but the safety margin was not uniformly obtained. The entire tumor was not embolized in 11 (2.9%). Regarding the tumor response at 2–3 months after cTACE in 303 tumors excluding those treated with combined radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or SR and lost to follow-up, 287 (94.7%) were classified into complete response, seven (2.3%) into partial response, and nine (3.0%) into stable disease. The mean follow-up period was 44.9 ± 27.6 months (range, 1–109) and the cumulative local tumor progression rates at 1, 3, 5, and 7 years were 17.8, 27.8, 32.0, and 36.0%, respectively. The 1-, 3-, 5-, and 7-year overall and recurrence-free survival rates in 175 patients, excluding those with Child–Pugh C class, who died of other malignancies, or who underwent combined RFA or hepatic resection, were 97.1 and 68.7, 82.8 and 34.9, 64.8 and 20.2, and 45.3 and 17.3%, respectively. Our results indicate the efficacy of superselective cTACE using guidance software for HCC within three lesions smaller than 3 cm.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prospective Randomized Study of Doxorubicin-Eluting-Bead Embolization in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of the PRECISION V Study
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found