- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antibacterial activity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles using biomolecules from Lignosus rhinocerotis and chitosan
Read this article at
Abstract
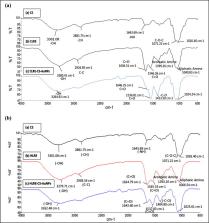
A simple, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly method is needed for synthesizing metal nanoparticles, including gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). In this study, AuNPs were synthesized with Lignosus rhinocerotis sclerotial extract (LRE) and chitosan (CS) as reducing and stabilizing agents, respectively. Different LRE concentrations from cold and hot water extraction (CWE and HWE, respectively) were used to reduce chloroauric acid (HAuCl 4) to form AuNPs. Positively charged chitosan stabilized AuNPs (CS-AuNPs) mediated by LRE exhibited a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) band at 533 nm. The CS-AuNPs synthesized using CWE had a smaller particle size (49.5 ± 6.7–82.4 ± 28.0 nm) compared to that of the HWE samples (80.3 ± 23.4–125.3 ± 41.5 nm), depending on LRE concentration. FTIR results suggested protein and polysaccharides in LRE were the sources of reducing power, reducing gold ions to AuNPs. CS-AuNPs were mostly spherical with higher LRE concentrations, whereas some triangular, pentagonal, irregular, and rod shaped AuNPs were observed at lower LRE concentrations. CS-AuNPs mediated by LRE displayed effective antibacterial activity against gram-negative ( Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli) and gram-positive bacteria ( Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus sp.). Thus, the biosynthesized AuNPs using LRE and chitosan provide opportunities for developing stable and eco-friendly nanoparticles with effective antibacterial properties.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Antibiotic resistance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found