- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of heparan sulfate and heparin oligosaccharides and NMR analysis: paving the way to a diverse library for glycobiologists†
Read this article at
Abstract

Abstract
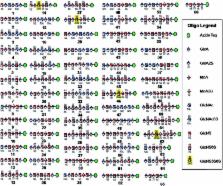
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a member of the glycosaminoglycans (GAG) family that plays essential roles in biological processes from animal sources. Heparin, a highly sulfated form of HS, is widely used as anticoagulant drug worldwide. The high diversity and complexity of HS and heparin represent a roadblock for structural characterization and biological activity studies. Access to structurally defined oligosaccharides is critical for the successful development of HS and heparin structure–activity relationships. In this study, a library of 66 HS and heparin oligosaccharides covering different sulfation patterns and sizes was prepared through an efficient method of chemoenzymatic synthesis. A systematic nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy study was firstly undertaken for every oligosaccharide in the library. In addition to the availability of different oligosaccharides, this work also provides spectroscopic data helpful for characterizing more complicated polysaccharide structures providing a safeguard to ensure the quality of the drug heparin. This HS/heparin library will be useful for activity screening and facilitate future structure–activity relationship studies.
Related collections
Author and article information
Notes
†Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Materials, detailed experimental protocols, supporting schemes and figures, synthetic methods, analytical data including HPLC profiles, mass and NMR spectra of synthesized oligosaccharides. See DOI: 10.1039/c7sc03541a