- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
SARS-CoV-2 Causes a Specific Dysfunction of the Kidney Proximal Tubule

Read this article at
Abstract
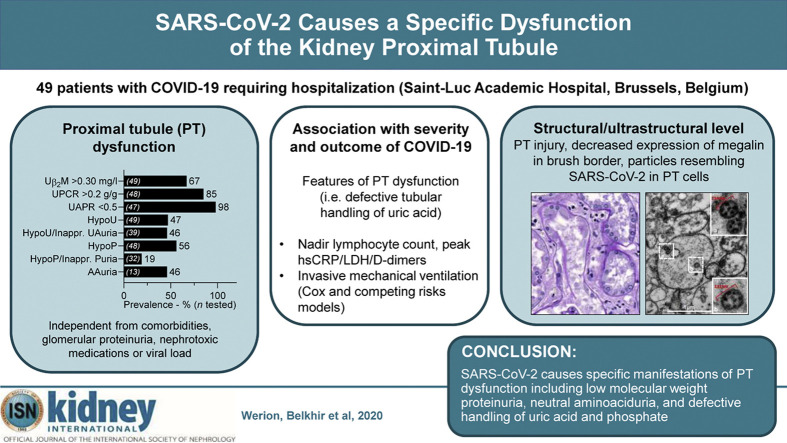
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is commonly associated with kidney damage, and the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor for SARS-CoV-2 is highly expressed in the proximal tubule cells. Whether patients with COVID-19 present specific manifestations of proximal tubule dysfunction remains unknown. To test this, we examined a cohort of 49 patients requiring hospitalization in a large academic hospital in Brussels, Belgium. There was evidence of proximal tubule dysfunction in a subset of patients with COVID-19, as attested by low-molecular-weight proteinuria (70-80%), neutral aminoaciduria (46%), and defective handling of uric acid (46%) or phosphate (19%). None of the patients had normoglycemic glucosuria. Proximal tubule dysfunction was independent of pre-existing comorbidities, glomerular proteinuria, nephrotoxic medications or viral load. At the structural level, kidneys from patients with COVID-19 showed prominent tubular injury, including in the initial part of the proximal tubule, with brush border loss, acute tubular necrosis, intraluminal debris, and a marked decrease in the expression of megalin in the brush border. Transmission electron microscopy identified particles resembling coronaviruses in vacuoles or cisternae of the endoplasmic reticulum in proximal tubule cells. Among features of proximal tubule dysfunction, hypouricemia with inappropriate uricosuria was independently associated with disease severity and with a significant increase in the risk of respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation using Cox (adjusted hazard ratio 6.2, 95% CI 1.9-20.1) or competing risks (adjusted sub-distribution hazard ratio 12.1, 95% CI 2.7-55.4) survival models. Thus, our data establish that SARS-CoV-2 causes specific manifestations of proximal tubule dysfunction and provide novel insights into COVID-19 severity and outcome.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found