- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as the risk mark in patients with type 2 diabetes combined with acute coronary syndrome: a cross-sectional study

Read this article at
Abstract
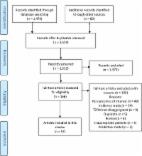
Chronic inflammation and dyslipidemia are important risk factors in developing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, such as coronary heart disease. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is one of the most dangerous syndromes in coronary heart disease. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is considered equal to coronary heart disease owing to the high cardiac risk induced by chronic inflammation and dyslipidemia. The neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) is a novel and straightforward marker that reflects inflammation and lipid metabolic disorder. However, few studies have been on the role of NHR in assessing the risk of ACS in T2DM patients. Here we analyzed NHR level in ACS patients with T2DM, exploring its predictive and diagnostic values. 211 hospitalized ACS patients with T2DM were recruited as the case group, and 168 hospitalized T2DM patients as the control group (all patients collected from 6/2020 to 12/2021 in Xiangya Hospital). Biochemical test results and echocardiograms, as well as demographic information such as age, BMI, diabetes mellitus, smoking, drinking, and history of hypertension, were recorded. Frequencies, percentages, means, and standard deviations were used to describe the data. The shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess the normality of the data. Normally distributed data were compared using the independent sample T-test, and non-normally distributed data were compared using Mann–Whitney U test. Correlation analysis was performed using the Spearman rank correlation test, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and multivariable logistic regression analysis were performed by SPSS version 24.0 (SPSS Inc) and GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software Inc). p < 0.05 was considered significant. In the study population, NHR was higher in patients with T2DM combined with ACS than in T2DM patients without ACS ( p < 0.001). After adjusting for BMI, alcohol consumption, and history of hypertension, multifactorial logistic regression analysis revealed that NHR is a risk factor for T2DM patients combined with ACS (OR 1.221, p = 0.0126). Correlation analysis on all ACS patients with T2DM showed that NHR level was positively correlated with cTnI (r = 0.437, p < 0.001), CK (r = 0.258, p = 0.001), CK-Mb (r = 0.447, p < 0.001), LDH (r = 384, p < 0.001), Mb (r = 0.320, p < 0.001), LA (r = 0.168, p = 0.042) and LV levels (r = 0.283, p = 0.001). And meanwhile, NHR level was negatively correlated with EF (r = − 0.327, p < 0.001) and FS levels (r = − 0.347, p < 0.001). ROC curve analysis showed that NHR ≧ 4.32 had a sensitivity of 65.45% and a specificity of 66.19% for predicting ACS in T2DM patients [area under the curve (AUC) = 0.722, p < 0.001]. Furthermore, in all ACS patients with T2DM, the diagnostic power of NHR was stronger in ST-segment elevated ACS patients (STE-ACS) than that in non-ST-segment elevated ACS patients (NSTE-ACS) ( p < 0.001). With its convenience and effective character, NHR could be a potential and new marker for predicting the presence, progression, and severity of ACS in T2DM population.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found