- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The spinning disc reactor for photocatalytic degradation: A systematic review
Read this article at
Abstract
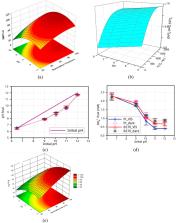
In recent years, the use of a horizontal spinning disc reactor (SDR) as a photocatalytic reactor for the degradation of various pollutants in aqueous solutions has increased. This study was searched based on the PRISMA method. Two autonomous researchers carried out for the relevant studies using Scopus, Web of Science (WOS), and Science Direct databases. The search terms expanded focusing on the performance of horizontal spinning disc photocatalytic reactor (SDPR). In this review article, the main objective of the effect of operational factors on the efficiency of the degradation of pollutants with changes in the type of light source (range of visible light and UV radiation), disc rotational speed, flow rate, initial concentration of pollutants, pH, type of disc structure and flow regime are considered. Current challenges in SDPR include issues such as limited mass transfer, uneven light distribution, and difficulties in scaling up. To overcome these challenges, improvements can be made by optimizing reactor design for better mass transfer, enhancing light distribution through advanced light sources or reactor configurations, and developing scalable models that maintain efficiency at larger scales. Additionally, the use of innovative materials and coatings could improve the overall performance of SDPR.
Related collections
Most cited references111
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Treatment technologies for emerging contaminants in water: A review
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found