- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
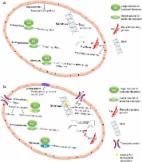
The emergence of metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) as a phytomedicine: A two-facet role in plant growth, nano-toxicity and anti-phyto-microbial activity
Rahul Bhattacharjee ,
Lamha Kumar ,
Nobendu Mukerjee ,
Uttpal Anand ,
Archna Dhasmana ,
Subham Preetam ,
Samudra Bhaumik ,
Sanjana Sihi ,
Sanjana Pal ,
Tushar Khare ,
Soham Chattopadhyay ,
Sally A. El-Zahaby ,
Athanasios Alexiou ,
Eapen P. Koshy ,
Vinay Kumar ,
Sumira Malik ,
Abhijit Dey ,
Jarosław Proćków
November 2022
November 2022
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Related collections
Most cited references228
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants.
Jian-Kang Zhu (2016)
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Animal Communication: When I’m Calling You, Will You Answer Too?
Neil Vickers (2017)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Metal nanoparticles: understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity
Yael Slavin, Jason Asnis, Urs Häfeli … (2017)