- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Data-based modeling for hypoglycemia prediction: Importance, trends, and implications for clinical practice
Read this article at
Abstract
Background and objective
Hypoglycemia is a key barrier to achieving optimal glycemic control in people with diabetes, which has been proven to cause a set of deleterious outcomes, such as impaired cognition, increased cardiovascular disease, and mortality. Hypoglycemia prediction has come to play a role in diabetes management as big data analysis and machine learning (ML) approaches have become increasingly prevalent in recent years. As a result, a review is needed to summarize the existing prediction algorithms and models to guide better clinical practice in hypoglycemia prevention.
Materials and methods
PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library were searched for relevant studies published between 1 January 2015 and 8 December 2022. Five hypoglycemia prediction aspects were covered: real-time hypoglycemia, mild and severe hypoglycemia, nocturnal hypoglycemia, inpatient hypoglycemia, and other hypoglycemia (postprandial, exercise-related).
Results
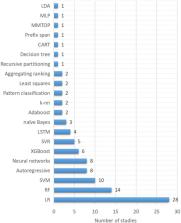
From the 5,042 records retrieved, we included 79 studies in our analysis. Two major categories of prediction models are identified by an overview of the chosen studies: simple or logistic regression models based on clinical data and data-based ML models (continuous glucose monitoring data is most commonly used). Models utilizing clinical data have identified a variety of risk factors that can lead to hypoglycemic events. Data-driven models based on various techniques such as neural networks, autoregressive, ensemble learning, supervised learning, and mathematical formulas have also revealed suggestive features in cases of hypoglycemia prediction.
Related collections
Most cited references124
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found