- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Multi-level barriers and facilitators to implementing a parenting intervention in prison, perceptions from deliverers and responsible managers: a mixed-methods study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Children of incarcerated parents run a high risk of poor health and own delinquency and positive parenting is vital for their healthy development. Internationally, parenting interventions for incarcerated parents suggest impacts on parenting and child behaviour outcomes. The intervention For Our Children’s Sake (FOCS), was developed for incarcerated parents in Sweden and evaluated in a controlled trial with a parallel process evaluation during 2019–2021. This study constitutes part of the process evaluation and aims to describe barriers and facilitators for the implementation of FOCS, and how the intervention targets parents’ needs, as perceived by delivering group leaders and responsible correctional inspectors.
Methods
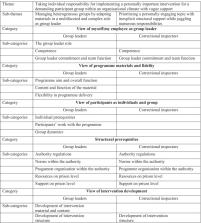
In this mixed-methods study, group leaders (n = 23) and correctional inspectors (n = 12) in both intervention and control group of the FOCS trial responded to a quantitative questionnaire regarding factors of importance for intervention implementation. Group leaders (n = 12) and correctional inspectors (n = 6) in the intervention group also participated in qualitative interviews. Quantitative data were analysed using descriptive statistics and comparison of means. Qualitative data were analysed inductively using qualitative content analysis.
Results
A synthesis of the quantitative and qualitative results showed that the topic of parenting and child issues in general was perceived as highly important to work with in prison, and FOCS to be an important programme in specific. At the same time, the implementation of FOCS was perceived as reliant on the individual engagement of group leaders and correctional inspectors and implementation was described as a struggle due to the scarce resources that were allowed for FOCS. Thus, additional resources and support from the Prison and Probation Service’s management were called for to facilitate implementation of FOCS, and to make it an automatic part of prison activities.
Conclusion
This study showed that there was high engagement among deliverers and managers for working with parenting in prison, where the need among parents has been described as great. Additional resources and support within the overall Prison and Probation Service, is vital to facilitate implementation of FOCS and make it sustainable within the prisons. The findings can be used to refine an implementations structure for similar interventions in the prison or similar settings.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found