- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical presentation, evaluation and case management of primary empty sella syndrome: a retrospective analysis of 10-year single-center patient data
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Primary Empty Sella (PES) syndrome is an increasingly common disorder, mostly diagnosed as an incidental finding during brain imaging scans. We intended to review the clinical management and hormonal profile of patients with PES.
Methods
The study included ten-year retrospective analysis of registry containing PES cases in the period 2007 to 2017, from a single tertiary care center. The keyword ‘primary empty sella’ was used to retrieve patient details from the radiology unit. The clinical and biochemical profile of PES patients was analyzed. Case management of PES patients and their rate of referral to endocrinologists was explored.
Results
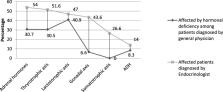
The registry had 765 cases with a male: female ratio of 1:3.8 suggesting female predominance by almost four times. Although not significant, the onset of disease was earlier for males [Mean ± standard deviation (SD) (46.7 years ±17.3 vs 48.8 years±14.1), p = 0.110]. Almost 79% of the cases were found as an incidental finding during Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Of the total PES cases, only 20% were referred to the endocrinologists and the rest were handled by general physicians. Only 1–2.5% of the cases were evaluated for gonadal, growth and adrenal hormones by the general physicians. The hormonal evaluation by the endocrinologists was also found to be sub-optimal. Headache and visual disturbances were the most common presenting complaints followed by menstrual abnormalities. Endocrine abnormalities like thyroid dysfunction, hyperprolactinemia, hypogonadism and hypocortisolism were highly prevalent among those assessed.
Conclusion
There is a gross under-evaluation of hormonal assessment and minimal case-referral to Endocrinologists. PES is associated with varying degrees of hormonal dysfunction, and hence early assessment and management is needed. Establishing a standard protocol for diagnosis and case management is essential with the involvement of a multidisciplinary team consisting of endocrinologists, neurologists, primary care phys icians and ophthalmologists.
Related collections
Most cited references19
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Primary empty sella: a comprehensive review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: the validity of cross-sectional neuroimaging signs.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found