- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Mitochondrial Citrate Carrier (SLC25A1) Sustains Redox Homeostasis and Mitochondrial Metabolism Supporting Radioresistance of Cancer Cells With Tolerance to Cycling Severe Hypoxia
Read this article at
Abstract
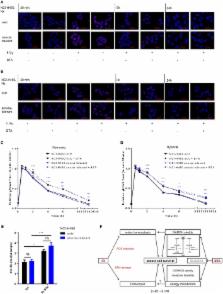
Pronounced resistance of lung cancer cells to radiotherapy and chemotherapy is a major barrier to successful treatment. Herein, both tumor hypoxia and the upregulation of the cellular antioxidant defense systems observed during malignant progression can contribute to radioresistance. We recently found that exposure to chronic cycling severe hypoxia/reoxygenation stress results in glutamine-dependent upregulation of cellular glutathione (GSH) levels and associated radiation resistance opening novel routes for tumor cell-specific radiosensitization. Here, we explored the role of the mitochondrial citrate carrier (SLC25A1) for the improved antioxidant defense of cancer cells with tolerance to acute and chronic severe hypoxia/reoxygenation stress and the use of pharmacologic SLC25A1 inhibition for tumor cell radiosensitization. Exposure to acute or chronic cycling severe hypoxia/reoxygenation stress triggered upregulated expression of SLC25A1 in lung cancer, prostate cancer, and glioblastoma cells in vitro. Interestingly, exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) further promoted SLC25A1 expression. Inhibition of SLC25A1 by 1,2,3-benzene-tricarboxylic acid (BTA) disturbed cellular and mitochondrial redox homeostasis, lowered mitochondrial metabolism, and reduced metabolic flexibility of cancer cells. Even more important, combining IR with BTA was able to overcome increased radioresistance induced by adaptation to chronic cycling severe hypoxia/reoxygenation stress. This radiosensitizing effect of BTA-treated cells was linked to increased reactive oxygen species and reduced DNA repair capacity. Of note, key findings could be reproduced when using the SLC25A1-inhibitor 4-Chloro-3-[[(3-nitrophenyl)amino]sulfonyl]-benzoic acid (CNASB). Moreover, in silico analysis of publically available databases applying the Kaplan–Meier plotter tool ( kmplot.com) revealed that overexpression of SLC25A1 was associated with reduced survival of lung cancer patients suggesting a potential link to aggressive cancers. We show that SLC25A1 can contribute to the increased antioxidant defense of cancer cells allowing them to escape the cytotoxic effects of IR. Since upregulation of SLC25A1 is induced by adverse conditions in the tumor environment, exposure to IR, or both pharmacologic inhibition of SLC25A1 might be an effective strategy for radiosensitization of cancer cells particularly in chronically hypoxic tumor fractions.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent carboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth and viability.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found