- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inhibition of the mitochondrial citrate carrier, Slc25a1, reverts steatosis, glucose intolerance, and inflammation in preclinical models of NAFLD/NASH
Read this article at
Abstract
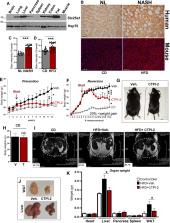
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its evolution to inflammatory steatohepatitis (NASH) are the most common causes of chronic liver damage and transplantation that are reaching epidemic proportions due to the upraising incidence of metabolic syndrome, obesity, and diabetes. Currently, there is no approved treatment for NASH. The mitochondrial citrate carrier, Slc25a1, has been proposed to play an important role in lipid metabolism, suggesting a potential role for this protein in the pathogenesis of this disease. Here, we show that Slc25a1 inhibition with a specific inhibitor compound, CTPI-2, halts salient alterations of NASH reverting steatosis, preventing the evolution to steatohepatitis, reducing inflammatory macrophage infiltration in the liver and adipose tissue, while starkly mitigating obesity induced by a high-fat diet. These effects are differentially recapitulated by a global ablation of one copy of the Slc25a1 gene or by a liver-targeted Slc25a1 knockout, which unravel dose-dependent and tissue-specific functions of this protein. Mechanistically, through citrate-dependent activities, Slc25a1 inhibition rewires the lipogenic program, blunts signaling from peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, a key regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, and inhibits the expression of gluconeogenic genes. The combination of these activities leads not only to inhibition of lipid anabolic processes, but also to a normalization of hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance as well. In summary, our data show for the first time that Slc25a1 serves as an important player in the pathogenesis of fatty liver disease and thus, provides a potentially exploitable and novel therapeutic target.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Inhibition Reduces Hepatic Steatosis but Elevates Plasma Triglycerides in Mice and Humans: A Bedside to Bench Investigation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found