- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Diet influences proliferation and stability of gut bacterial populations in herbivorous lepidopteran larvae

Read this article at
Abstract
Animals have ubiquitous associations with microorganisms, but microbial community composition and population dynamics can vary depending upon many environmental factors, including diet. The bacterial communities present in caterpillar (Lepidoptera) guts are highly variable, even among individuals of a species. Across lepidopteran species, it is unclear if the variation in their gut bacterial communities is due to ingested bacteria with diets or responses of gut bacteria to their diet. In this study, we aimed to understand whether bacteria establish and persist in the lepidopteran gut or just pass through the gut with food. We also examined whether bacterial establishment in lepidopteran guts depended on diet. We conducted a series of experiments using axenic and gnotobiotic insect rearing methods to address these objectives. We found that bacteria were established and maintained without replacement through the larval instars of the fall armyworm ( Spodoptera frugiperda) and corn earworm ( Helicoverpa zea). Gut bacterial titers increased when larvae were fed gamma-irradiated corn leaves but decreased when fed a wheat germ artificial diet. However, bacterial titers of larvae fed on a pinto bean artificial diet were similar to those consuming intact plants. We also observed that microbial titers of fall armyworm and other folivorous larvae were positively related to the host body size throughout larval development. Collectively, these results suggest that the populations of bacteria present in caterpillar guts are not simply a transient community passing through the system, but rather are a dynamic component of the caterpillar gut. Sensitivity of bacterial populations to the type of diet fed to lepidopterans suggests that not all diets are equally useful for reducing variance in community structure and interpreting insect-microbe interactions.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Multiorganismal insects: diversity and function of resident microorganisms.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
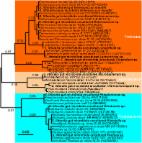
Biodiversity and Activity of the Gut Microbiota across the Life History of the Insect Herbivore Spodoptera littoralis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found