- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Single-cell transcriptome sequencing: recent advances and remaining challenges
Read this article at
Abstract
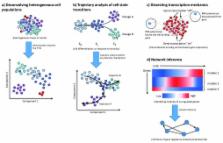
Single-cell RNA-sequencing methods are now robust and economically practical and are becoming a powerful tool for high-throughput, high-resolution transcriptomic analysis of cell states and dynamics. Single-cell approaches circumvent the averaging artifacts associated with traditional bulk population data, yielding new insights into the cellular diversity underlying superficially homogeneous populations. Thus far, single-cell RNA-sequencing has already shown great effectiveness in unraveling complex cell populations, reconstructing developmental trajectories, and modeling transcriptional dynamics. Ongoing technical improvements to single-cell RNA-sequencing throughput and sensitivity, the development of more sophisticated analytical frameworks for single-cell data, and an increasing array of complementary single-cell assays all promise to expand the usefulness and potential applications of single-cell transcriptomic profiling.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nature, nurture, or chance: stochastic gene expression and its consequences.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals bimodality in expression and splicing in immune cells
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found