- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Novel Ultrasound Robot with Force/torque Measurement and Control for Safe and Efficient Scanning
Read this article at
Abstract
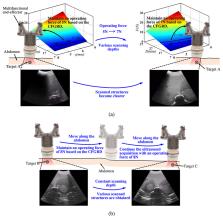
Medical ultrasound is of increasing importance in medical diagnosis and intraoperative assistance and possesses great potential advantages when integrated with robotics. However, some concerns, including the operation efficiency, operation safety, image quality, and comfort of patients, remain after introducing robotics into medical ultrasound. In this paper, an ultrasound robot integrating a force control mechanism, force/torque measurement mechanism, and online adjustment method, is proposed to overcome the current limitations. The ultrasound robot can measure operating forces and torques, provide adjustable constant operating forces, eliminate great operating forces introduced by accidental operations, and achieve various scanning depths based on clinical requirements. The proposed ultrasound robot would potentially facilitate sonographers to find the targets quickly, improve operation safety and efficiency, and decrease patients’ discomfort. Simulations and experiments were carried out to evaluate the performance of the ultrasound robot. Experimental results show that the proposed ultrasound robot is able to detect operating force in the z-direction and torques around the x- and y- directions with errors of 3.53% F.S., 6.68% F.S., and 6.11% F.S., respectively, maintain the constant operating force with errors of less than 0.57N, and achieve various scanning depths for target searching and imaging. This proposed ultrasound robot has good performance and would potentially be used in medical ultrasound.
Related collections
Most cited references24

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
SonoNet: Real-Time Detection and Localisation of Fetal Standard Scan Planes in Freehand Ultrasound
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found