- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
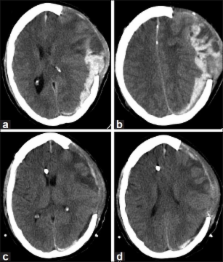
Spontaneous acute subdural hematoma due to fondaparinux: Report of two cases
case-report
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
Background:
Spontaneous acute subdural hematomas (SDHs) are rare. Risk factors for development of these hematomas include conditions such as hypertension, vascular abnormalities such as aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation, or consumption of anticoagulants.
Case Description:
Here, the authors report two patients who suffered from spontaneous acute SDH while taking fondaparinux for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. One patient suffered from a remote episode of traumatic brain injury and underwent a decompressive craniectomy 3 weeks prior to presentation, whereas the other patient had been self-medicating with aspirin.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fondaparinux compared with enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after hip-fracture surgery.
, B Eriksson, Manuel Bauer … (2001)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fondaparinux compared with enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after elective major knee surgery.
A Turpie, Bengt I Eriksson, M Lassen … (2001)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical patients.
Giancarlo Agnelli (2004)