- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Proposing new early detection indicators for pancreatic cancer: Combining machine learning and neural networks for serum miRNA-based diagnostic model
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a lethal malignancy that ranks seventh in terms of global cancer-related mortality. Despite advancements in treatment, the five-year survival rate remains low, emphasizing the urgent need for reliable early detection methods. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a group of non-coding RNAs involved in critical gene regulatory mechanisms, have garnered significant attention as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer (PC). Their suitability stems from their accessibility and stability in blood, making them particularly appealing for clinical applications.
Methods
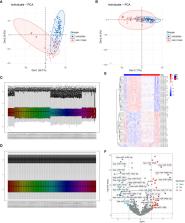
In this study, we analyzed serum miRNA expression profiles from three independent PC datasets obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. To identify serum miRNAs associated with PC incidence, we employed three machine learning algorithms: Support Vector Machine-Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE), Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO), and Random Forest. We developed an artificial neural network model to assess the accuracy of the identified PC-related serum miRNAs (PCRSMs) and create a nomogram. These findings were further validated through qPCR experiments. Additionally, patient samples with PC were classified using the consensus clustering method.
Results
Our analysis revealed three PCRSMs, namely hsa-miR-4648, hsa-miR-125b-1-3p, and hsa-miR-3201, using the three machine learning algorithms. The artificial neural network model demonstrated high accuracy in distinguishing between normal and pancreatic cancer samples, with verification and training groups exhibiting AUC values of 0.935 and 0.926, respectively. We also utilized the consensus clustering method to classify PC samples into two optimal subtypes. Furthermore, our investigation into the expression of PCRSMs unveiled a significant negative correlation between the expression of hsa-miR-125b-1-3p and age.
Conclusion
Our study introduces a novel artificial neural network model for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, carrying significant clinical implications. Furthermore, our findings provide valuable insights into the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer and offer potential avenues for drug screening, personalized treatment, and immunotherapy against this lethal disease.
Related collections
Most cited references67
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found