- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Review: Detection and quantification of proteins in human urine
Read this article at
Abstract
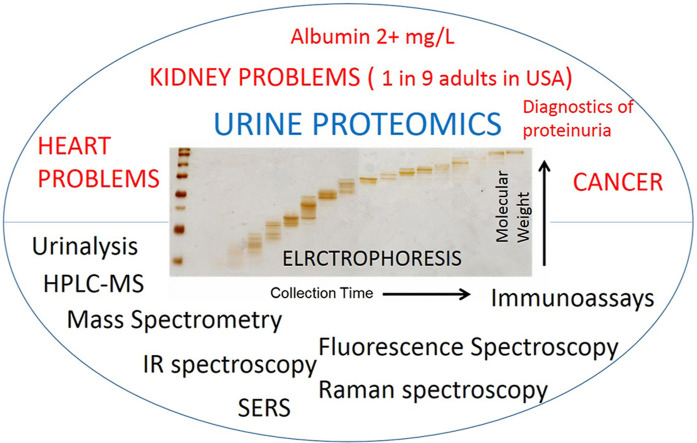
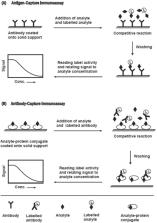
Extensive medical research showed that patients, with high protein concentration in urine, have various kinds of kidney diseases, referred to as proteinuria. Urinary protein biomarkers are useful for diagnosis of many health conditions – kidney and cardio vascular diseases, cancers, diabetes, infections. This review focuses on the instrumental quantification (electrophoresis, chromatography, immunoassays, mass spectrometry, fluorescence spectroscopy, the infrared spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy) of proteins (the most of all albumin) in human urine matrix. Different techniques provide unique information on what constituents of the urine are. Due to complex nature of urine, a separation step by electrophoresis or chromatography are often used for proteomics study of urine. Mass spectrometry is a powerful tool for the discovery and the analysis of biomarkers in urine, however, costs of the analysis are high, especially for quantitative analysis. Immunoassays, which often come with fluorescence detection, are major qualitative and quantitative tools in clinical analysis. While Infrared and Raman spectroscopies do not give extensive information about urine, they could become important tools for the routine clinical diagnostics of kidney problems, due to rapidness and low-cost. Thus, it is important to review all the applicable techniques and methods related to urine analysis. In this review, a brief overview of each technique’s principle is introduced. Where applicable, research papers about protein determination in urine are summarized with the main figures of merits, such as the limit of detection, the detectable range, recovery and accuracy, when available.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Urinary protein biomarkers are useful for diagnosis of many health conditions – kidney and cardio vascular diseases, cancers, diabetes, infections.
-
•
Liquid chromatography – mass spectroscopy is a powerful tool for urine proteomics, but used mostly in research labs. Many new biomarkers were discovered by this technique.
-
•
Immunoassays are widely used in both clinical and bio-analytical laboratories.
-
•
Infrared and Raman spectroscopies are promising tools for analysis of urine and di-agnostics due to relatively simple sample preparation, low-cost and short time of analysis.
Related collections
Most cited references180
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
SERS: Materials, applications, and the future
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found