- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogs: Recent Advances, New Possibilities, and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
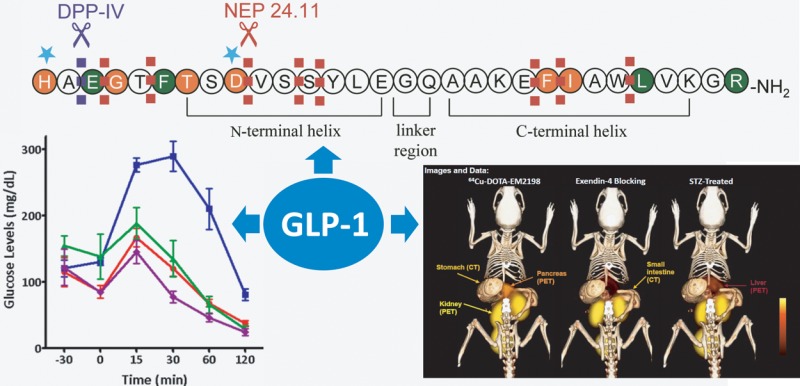
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin that plays important physiological roles in glucose homeostasis. Produced from intestine upon food intake, it stimulates insulin secretion and keeps pancreatic β-cells healthy and proliferating. Because of these beneficial effects, it has attracted a great deal of attention in the past decade, and an entirely new line of diabetic therapeutics has emerged based on the peptide. In addition to the therapeutic applications, GLP-1 analogs have demonstrated a potential in molecular imaging of pancreatic β-cells; this may be useful in early detection of the disease and evaluation of therapeutic interventions, including islet transplantation. In this Perspective, we focus on GLP-1 analogs for their studies on improvement of biological activities, enhancement of metabolic stability, investigation of receptor interaction, and visualization of the pancreatic islets.
Related collections
Most cited references120
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: many differences, few similarities.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Isolation and characterization of exendin-4, an exendin-3 analogue, from Heloderma suspectum venom. Further evidence for an exendin receptor on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.