- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Integrating Interleukin-6 into depression diagnosis and treatment
Read this article at
Abstract
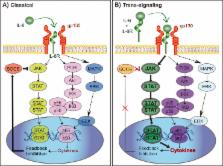
There is growing evidence of a relationship between inflammation and psychiatric illness. In particular, the cytokine Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been linked to stress-related disorders such as depression and anxiety. Here we discuss evidence from preclinical and clinical studies examining the role of IL-6 in mood disorders. We focus on the functional role of peripheral and central release of IL-6 on the development of stress susceptibility and depression-associated behavior. By examining the contribution of both peripheral and central IL-6 to manifestations of stress-related symptomatology, we hope to broaden the way the field thinks about diagnosing and treating mood disorders.
Related collections
Most cited references78
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found