- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Adsorption of Rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution onto acid treated banana peel: Response surface methodology, kinetics and isotherm studies
Read this article at
Abstract
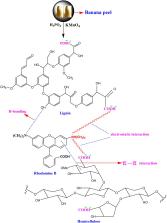
The adsorption of rhodamine B (RhB) using acid modified banana peels has been examined. Chemical characteristics of the adsorbents were observed in order to determine active functional groups. The major functional groups on the surface were OH, C = O, C = C and C-O-C. Interactions between operational parameters were studied using the central composite design (CCD) of response surface methodology (RSM). The predictions of the model output indicated that operational factors influenced responses at a confidence level of 95% (P<0.05). The optimum conditions for adsorption were pH 2 at a 0.2 g/L dose within 60 minutes of contact time. Isotherm studies were carried out using the optimized process variables. The data revealed that RhB adsorption fitted the Langmuir isotherm equation while the reduction of COD followed the Freundlich isotherm. Kinetic experiments fitted the pseudo second order model for RhB removal and COD reduction. The adsorption mechanism was not the only rate controlling step. Diffusion through the boundary layer described the pattern of adsorption.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Application of chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater: a review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found