- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Porphyrin–Nanocarbon Complexes to Control the Photodegradation of Rhodamine
Read this article at
Abstract

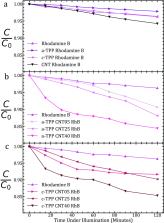
Porphyrin–nanocarbon systems were used to generate a photocatalyst for the control of rhodamine B and rhodamine 6G photodegradation. Carboxylic functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes ( o-MWCNTs) were decorated by two different porphyrin moieties: 5-(4-aminophenyl)-10,15,20-(triphenyl)porphyrin (a-TPP) with an amine linker and 5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-10,15,20-(triphenyl)porphyrin (c-TPP) with a carboxyl linker to the o-MWCNT, respectively, with their photocatalyst performances investigated. The optical properties of the mixed nanocomposite materials were investigated to reveal the intrinsic energy levels and mechanisms of degradation. The charge-transfer states of the o-MWCNTs were directly correlated with the performance of the complexes as well as the affinity of the porphyrin moiety to the o-MWCNT anchor, thus extending our understanding of energy-transfer kinetics in porphyrin–CNT systems. Both a-TPP and c-TPP o-MWCNT complexes offered improved photocatalytic performance for both RhB and Rh6G compared to the reference o-MWCNTs and both porphyrins in isolated form. The photocatalytic performance improved with higher concentration of o-MWCNTs in the complexed sample, indicating the presence of greater numbers of −H/–OH groups necessary to more efficient photodegradation. The large presence of the −H/–OH group in the complexes was expected and was related to the functionalization of the o-MWCNTs needed for high porphyrin attachment. However, the photocatalytic efficiency was affected at higher o-MWCNT concentrations due to the decomposition of the porphyrins and changes to the size of the CNT agglomerates, thus reducing the surface area of the reactant. These findings demonstrate a system that displays solar-based degradation of rhodamine moieties that are on par, or an improvement to, state-of-the-art organic systems.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanocarbons for Biology and Medicine: Sensing, Imaging, and Drug Delivery
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found