- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Intraocular Implantable Collamer Lens with a Central Hole Implantation: Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Outcomes
Read this article at
Abstract
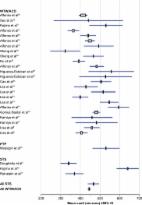
This review summarizes the available literature and provides updates on the efficacy, safety, and patient outcomes of phakic intraocular lens implantation using implantable collamer lens (ICL), with a focus on newer models with a central port (EVO/EVO+ Visian Implantable Collamer Lens, STAAR Surgical Inc.). All studies included in this review were identified from the PubMed database and were reviewed for relevancy of their topic. Data on hole-ICL implantation performed between October 2018 and October 2022 in 3399 eyes showed a weighted average efficacy index of 1.03 and a weighted average safety index of 1.19 within an average follow-up of 24.7 months. The incidence of complications such as elevated intraocular pressure, cataract, and corneal endothelial cell loss was low. Moreover, both quality of vision and quality of life improved after ICL implantation, confirming the benefits of this procedure. In conclusion, ICL implantation is a promising refractive surgery alternative to laser vision correction with excellent efficacy, safety, and patient outcomes.
Related collections
Most cited references97
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Meta-analysis and review: effectiveness, safety, and central port design of the intraocular collamer lens
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
United States Food and Drug Administration clinical trial of the Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) for moderate to high myopia: three-year follow-up.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found