- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater

Read this article at
ABSTRACT
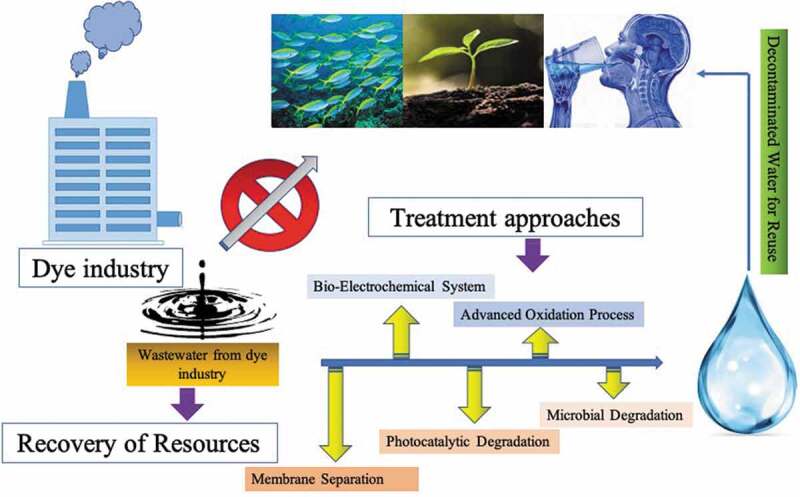
Rapid industrialization has provided comforts to mankind but has also impacted the environment harmfully. There has been severe increase in the pollution due to several industries, in particular due to dye industry, which generate huge quantities of wastewater containing hazardous chemicals. Although tremendous developments have taken place for the treatment and management of such wastewater through chemical or biological processes, there is an emerging shift in the approach, with focus shifting on resource recovery from such wastewater and also their management in sustainable manner. This review article aims to present and discuss the most advanced and state-of-art technical and scientific developments about the treatment of dye industry wastewater, which include advanced oxidation process, membrane filtration technique, microbial technologies, bio-electrochemical degradation, photocatalytic degradation, etc. Among these technologies, microbial degradation seems highly promising for resource recovery and sustainability and has been discussed in detail as a promising approach. This paper also covers the challenges and future perspectives in this field.
GRAPHICAL ABSTARCT
Related collections
Most cited references154
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.