- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A PI3K p110β–Rac signalling loop mediates Pten-loss-induced perturbation of haematopoiesis and leukaemogenesis
Read this article at
Abstract
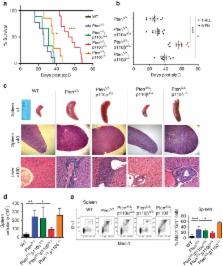
The tumour suppressor PTEN, which antagonizes PI3K signalling, is frequently inactivated in haematologic malignancies. In mice, deletion of PTEN in haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) causes perturbed haematopoiesis, myeloproliferative neoplasia (MPN) and leukaemia. Although the roles of the PI3K isoforms have been studied in PTEN-deficient tumours, their individual roles in PTEN-deficient HSCs are unknown. Here we show that when we delete PTEN in HSCs using the Mx1–Cre system, p110β ablation prevents MPN, improves HSC function and suppresses leukaemia initiation. Pharmacologic inhibition of p110β in PTEN-deficient mice recapitulates these genetic findings, but suggests involvement of both Akt-dependent and -independent pathways. Further investigation reveals that a p110β–Rac signalling loop plays a critical role in PTEN-deficient HSCs. Together, these data suggest that myeloid neoplasia driven by PTEN loss is dependent on p110β via p110β–Rac-positive-feedback loop, and that disruption of this loop may offer a new and effective therapeutic strategy for PTEN-deficient leukaemia.
Abstract
 The tumor suppressor PTEN antagonizes the PI3K signalling pathway and is frequently
inactivated in haematological malignancies. Here, the authors unravel the main contribution
of the PI3K isoform p110ß to leukemic transformation driven by PTEN-loss.
The tumor suppressor PTEN antagonizes the PI3K signalling pathway and is frequently
inactivated in haematological malignancies. Here, the authors unravel the main contribution
of the PI3K isoform p110ß to leukemic transformation driven by PTEN-loss.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in acute myeloid leukemia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pten dependence distinguishes haematopoietic stem cells from leukaemia-initiating cells.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found