- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
miRNA 933 Expression by Endothelial Cells is Increased by 27-Hydroxycholesterol and is More Prevalent in Plasma from Dementia Patients
Read this article at
Abstract
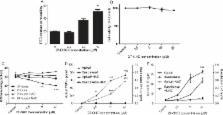
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) etiology is complex; gene and environmental risk factors may interact to predispose to disease. From single nucleotide polymorphism analyses and genome-wide association studies, a number of candidate risk genes for the onset of AD have been identified and cluster around lipid metabolism and inflammation. We hypothesized that endothelial cells which line the blood-brain barrier are likely to be critical mediators of systemic metabolism within the brain. Therefore, we have studied the effect of 27 hydroxycholesterol (27-OHC) on microvascular endothelial cell (HMVEC) redox state, inflammatory cytokine secretion, and microRNA (miR) expression. Using a transwell method, we have studied directional secretion profiles for the proinflammatory cytokines TNF α and IL-6 and confirmed that 27-OHC induces discrete and directional inflammatory molecular signatures from HMVEC. The lipids caused depletion of cellular glutathione and cytokine secretion is HMVEC-redox state-dependent. Discovery miR expression change in HMVEC with and without 27-OHC treatment was undertaken. We selected three genes for further analysis by qPCR; miR-144 and 146 expression, which are anti-inflammatory and redox regulating modulators, were not affected significantly by 27-OHC. However, increased expression of a putative neurotrophic regulatory factor miR933 in HMVEC with 27-OHC was confirmed by qPCR. In plasma from patients with dementia, all three miR were found at significantly elevated levels compared to healthy older adults. These data highlight that 27-OHC has an important regulatory effect on endothelial microvascular cells to increase expression of a miR (–933) and secretion of inflammatory cytokines that are elevated in plasma from dementia patients.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Extracellular miRNAs: the mystery of their origin and function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found