- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Herbal Tea for the Management of Pharyngitis: Inhibition of Streptococcus pyogenes Growth and Biofilm Formation by Herbal Infusions
Read this article at
Abstract
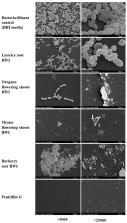
Herbal teas are becoming popular as functional beverages due to their various health promotional properties. This study aimed at assessing 13 hot water infusions (HWIs) from different herbs against streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat). Licorice root exhibited the lowest minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of 1.56 mg/mL, followed by barberry root, thyme, and oregano flowering shoots, with a MIC of 3.13 mg/mL. At their respective minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBC), licorice showed the bactericidal effect on S. pyogenes within 12 h after exposure while others need 24 h for a similar outcome. The HWIs exhibited inhibitory activity on biofilm formation, ranging from 1.56 to 6.25 mg/mL, which confirmed by ruptured cells or clusters of dead cell debris observed in scanning electron microscope (SEM). Overall, non-toxic concentrations of efficacious HWIs from licorice root, barberry root, thyme, and oregano flowering shoots may provide potential sources for developing herbal teas or biomedicine for the management of S. pyogenes infections.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence of streptococcal pharyngitis and streptococcal carriage in children: a meta-analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Evaluation of antioxidant activity, total phenols and phenolic compounds in thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), sage (Salvia officinalis L.), and marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) extracts
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found