- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MALAT1/miR-15b-5p/ MAPK1 mediates endothelial progenitor cells autophagy and affects coronary atherosclerotic heart disease via mTOR signaling pathway
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective: Present study focused on the influence of lncRNA MALAT1 on coronary atherosclerotic heart disease (CAD) by regulating miR-15b-5p/ MAPK1 and mTOR signaling pathway.
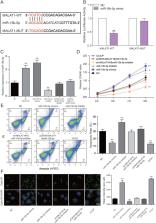
Method: Differentially expressed genes and activated pathway were investigated through bioinformatics analysis. QRT-PCR was conducted to verify expression of MALAT1, miR-15b-5p and MAPK1 in CAD blood samples and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). In addition, the interactions among MALAT1, miR-15b-5p and MAPK1 were revealed by Luciferase reporter assay. Cell autophagy of EPCs was examined by Cyto-ID Autophagy Detection Kit and transmission electron microscope. MTT assay and flow cytometry were carried out to assess cell viability and apoptosis in different interference conditions. Western blot was performed to testify the expression of pERK1/2 (MAPK1), phosphorylated mTOR, ATG1 and LC3-II. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) were detected by qRT-PCR. Finally, the effect of lncRNA MALAT1 on cell autophagy and atherogenesis was tested in vivo.
Results: MALAT1 was overexpressed in CAD blood samples and EPCs. Knockdown of MALAT1 and MAPK1 promoted cell viability, autophagy and further suppressed the development of CAD. Antago MALAT1 protects mice against atherosclerosis.
Conclusion: LncRNA MALAT1 inhibited EPCs autophagy and increased cell viability while repressed apoptosis of CAD via activating mTOR signaling pathway.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
TOR, a Central Controller of Cell Growth

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
LncRNA CAIF inhibits autophagy and attenuates myocardial infarction by blocking p53-mediated myocardin transcription
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found