- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prognostic Value of Long Non-Coding RNA HULC and MALAT1 Following the Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
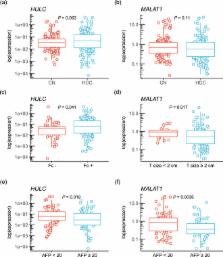
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were shown to be the crucial regulators of the many diseases. In this study, the expressions of lncRNAs were investigated in resected 158 hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) to evaluate the effects of their expression levels on prognosis. The expression levels of HULC and MALAT1 were shown to be significantly higher in the normal background tissue of HCC than those in the normal liver tissue of metastatic liver tumor without hepatitis ( HULC: fold change 14.9, P = 1.7e-06; MALAT1: fold change 17.5, P = 1.2e-06. The formation of capsule was shown to be correlated with the increased expression of HULC ( P = 0.041), while the size of HCC under 2 cm was correlated with a decrease in MALAT1 expression ( P = 0.019). The levels of serum alpha-fetoprotein above 20 ng/mL indicated a decreased expression of both HULC and MALAT1 ( HULC: P = 0.017; MALAT1: P = 0.0036). The increase in the expression levels of MALAT1 in HCC tissues was significantly correlated with better overall survival ( HULC: P = 0.099, MALAT1: P = 0.028). Thus, the expression of these lncRNAs in HCC potentially correlates with the HCC malignancy and they represent potential prognostic biomarkers of the resected HCC.
Related collections
Most cited references19
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found