- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Proteinases in the joint: clinical relevance of proteinases in joint destruction
review-article
31 October 2007
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
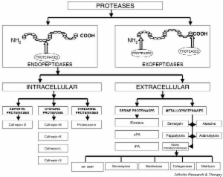
Proteinases are involved in essential steps in cartilage and bone homeostasis. Consequently, efforts have been made to establish their potential role in the pathology of rheumatic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and spondyloarthritis. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are sensitive markers of disease severity and response to treatment, and therefore they have potential in the assessment of rheumatic diseases. Despite disappointing early results with synthetic inhibitors of MMPs, there is still much scope for developing effective and safe MMPs inhibitors, and consequently to deliver new options to inhibit joint destruction.
Related collections
Most cited references80
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neutrophil serine proteases: specific regulators of inflammation.
Christine Pham (2006)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
