- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Hijacking the Host Immune Cells by Dengue Virus: Molecular Interplay of Receptors and Dengue Virus Envelope
Read this article at
Abstract
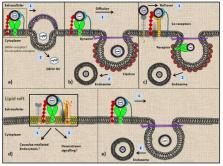
Dengue virus (DENV) is one of the lethal pathogens in the hot climatic regions of the world and has been extensively studied to decipher its mechanism of pathogenesis and the missing links of its life cycle. With respect to the entry of DENV, multiple receptors have been recognized in different cells of the human body. However, scientists still argue whether these identified receptors are the exclusive entry mediators for the virus. Adding to the complexity, DENV has been reported to be infecting multiple organ types in its human host. Also, more than one receptor in a particular cell has been discerned to take part in mediating the ingress of DENV. In this review, we aim to discuss the different cells of the human immune system that support DENV infection and their corresponding receptors that DENV deploy to gain access to the cells.
Related collections
Most cited references81
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Signalling through C-type lectin receptors: shaping immune responses
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dengue virus pathogenesis: an integrated view.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found