- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Maternal childbirth experience and time of delivery: a retrospective 7-year cohort study of 105 847 parturients in Finland
Read this article at
Abstract
Setting
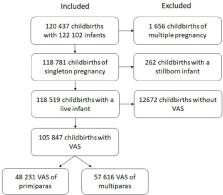
Childbirth in the four Helsinki and Uusimaa Hospital District hospitals, Finland, from 2012 to 2018.
Results
The major difference in average childbirth experience measured by VAS was between primiparas (8.03; 95% CI 8.01 to 8.04) and multiparas (8.47; 95% CI 8.45 to 8.48). Risk ratio (RR) of the low VAS (≤5) was 2.3 when primiparas were compared with multiparas. Differences in VAS between distinct periods were found in two stages: annual and time of day. The decrease in VAS from 2012–2016 to 2017–2018 in primiparas was from 7.97 (95% CI 7.95 to 7.99) to 7.80 (95% CI 7.77 to 7.83) and from 2014–2016 to 2017–2018 in multiparas from 8.60 (95% CI 8.58 to 8.61) to 8.49 (95% CI 8.47 to 8.52). Corresponding RRs of low VAS were 1.3 for primiparas and 1.2 for multiparas. Hourly differences in VAS were detected in primiparas between office hours 08:00–15:59 (7.97; 95% CI 7.94 to 7.99) and other times (night 00:00–07:59; 7.91; 95% CI 7.88 to 7.94; and evening 16:00–23:59; 7.90; 95% CI 7.87 to 7.92). In multiparas differences in VAS were detected between evening (8.52; 95% CI 8.50 to 8.54) and other periods (night; 8.56; 95% CI 8.54 to 9.58; and office hours; 8.57; 95% CI 8.55 to 8.59).
Conclusion
The maternal childbirth experience depended on the time of delivery. Giving birth during the evening led to impaired childbirth experience in both primiparas and multiparas, compared with delivery at other times. The impact of labour induction on childbirth experience should be further examined. The reorganisation of delivery services and the reduction of birth preparations might affect annual VAS. VAS is a simple method of measuring the complex entity of childbirth experience, and our results indicate its ability to capture temporal variation.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pain and women's satisfaction with the experience of childbirth: a systematic review.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trends in postpartum hemorrhage in high resource countries: a review and recommendations from the International Postpartum Hemorrhage Collaborative Group
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found