- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effectiveness of polyherbal formulations for the treatment of type 2 D iabetes mellitus - A systematic review and meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The mortality and morbidity rate of diabetes patients is increasing worldwide which requires an ideal treatment to prevent the disease worsening. Traditional medicine is gaining more attention in diabetes due to its efficacy and safety. We, therefore performed a systematic review study of clinical trials to assess the comparative effect of polyherbal formulations in type 2 D iabetes mellitus.
Objectives
To find the effectiveness of polyherbal formulations in blood sugar and lipid level for type 2 D iabetes mellitus.
Material and methods
PubMed, Scopus and CINAHL databases for clinical trials investigating the effect of polyherbal formulations in Type 2 D iabetes mellitus patients were searched. Meta-analysis of eligible trials was conducted employing Revman 5.2 software.
Results
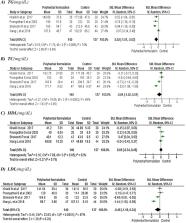
Fourteen randomized controlled trials were found eligible for meta-analysis. Meta-analysis of findings showed a significant effect of polyherbal formulations on blood sugar level compared to control group. The estimated standard mean changes at 95% confidence interval, following polyherbal formulations treatment were −0.59, (−0.91 to – 0.27) mg/dL; for fasting blood sugar(p < 0.001), −0.69, (−1.18 to −0.21) mg/dL; for postprandial blood sugar (p = 0.005) and −0.46, (−0.88 to −0.04) gm%; for glycated haemoglobin (p = 0.03). The reduction in postprandial sugar and glycated haemoglobin was statistically significant with polyherbal formulations compared to metformin treatment but not for fasting sugar. Similarly in lipid profile the reduction for total cholesterol and triglycerides was statistically significant with polyherbal formulations compared to control group but was not significant for HDL and LDL whereas in other group of polyherbal formulations and metformin only HDL was favouring polyherbal formulations.
Conclusion
Polyherbal formulations occurred to be effective in lowering blood sugar level in Type 2 diabetes but their further efficacy in managing diabetes needs to be validated. Therefore, a qualitative, long term, randomized placebo-controlled trials of adequate sample size are necessary to determine the efficacy of polyherbal formulation in managing diabetes.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found