- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Passive Sensor Integration for Vehicle Self-Localization in Urban Traffic Environment †
Read this article at
Abstract
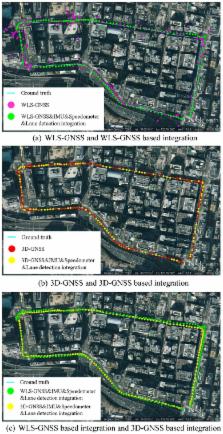
This research proposes an accurate vehicular positioning system which can achieve lane-level performance in urban canyons. Multiple passive sensors, which include Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers, onboard cameras and inertial sensors, are integrated in the proposed system. As the main source for the localization, the GNSS technique suffers from Non-Line-Of-Sight (NLOS) propagation and multipath effects in urban canyons. This paper proposes to employ a novel GNSS positioning technique in the integration. The employed GNSS technique reduces the multipath and NLOS effects by using the 3D building map. In addition, the inertial sensor can describe the vehicle motion, but has a drift problem as time increases. This paper develops vision-based lane detection, which is firstly used for controlling the drift of the inertial sensor. Moreover, the lane keeping and changing behaviors are extracted from the lane detection function, and further reduce the lateral positioning error in the proposed localization system. We evaluate the integrated localization system in the challenging city urban scenario. The experiments demonstrate the proposed method has sub-meter accuracy with respect to mean positioning error.
Related collections
Most cited references70
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
GOLD: a parallel real-time stereo vision system for generic obstacle and lane detection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Performance Enhancement of MEMS-Based INS/GPS Integration for Low-Cost Navigation Applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found