- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Emerging New Approaches in Desensitization: Targeted Therapies for HLA Sensitization
Read this article at
Abstract
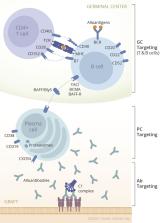
There is an urgent need for therapeutic interventions for desensitization and antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) in sensitized patients with preformed or de novo donor-specific HLA antibodies (DSA). The risk of AMR and allograft loss in sensitized patients is increased due to preformed DSA detected at time of transplant or the reactivation of HLA memory after transplantation, causing acute and chronic AMR. Alternatively, de novo DSA that develops post-transplant due to inadequate immunosuppression and again may lead to acute and chronic AMR or even allograft loss. Circulating antibody, the final product of the humoral immune response, has been the primary target of desensitization and AMR treatment. However, in many cases these protocols fail to achieve efficient removal of all DSA and long-term outcomes of patients with persistent DSA are far worse when compared to non-sensitized patients. We believe that targeting multiple components of humoral immunity will lead to improved outcomes for such patients. In this review, we will briefly discuss conventional desensitization methods targeting antibody or B cell removal and then present a mechanistically designed desensitization regimen targeting plasma cells and the humoral response.
Related collections
Most cited references217
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab Monotherapy in Multiple Myeloma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found