- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The human umbilical cord stem cells improve the viability of OA degenerated chondrocytes

Read this article at
Abstract
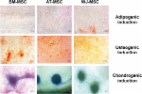
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects a large number of patients; however, human umbilical cord stem cells exhibit therapeutic potential for treating OA. The aim of the present study was to explore the interaction between human umbilical cord stem cells and degenerated chondrocytes, and the therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord stem cells on degenerated chondrocytes. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) were harvested from human umbilical cords, and flow cytometry was used to analyze the surface antigen markers, in addition, chondrogenic, osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation on the cells was investigated. OA cells at P3 were cocultured with hUC-MSCs in a separated co-culture system, and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot were used to evaluate the mRNA, and protein expression of collagen type II (Col2), SRY-box 9 (sox-9) and aggrecan. The level of inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, were analyzed by ELISA in the supernatant. hUC-MSCs grow in a fibroblastic shape with stable proliferation. hUC-MSCs expressed cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), CD73, CD90, CD105; while did not express CD34, CD45, CD106, CD133. After multi-induction, hUC-MSCs were able to differatiate into adipogenic, osteogenic and chondrogenic lineage. hUC-MSCs inhibited the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13, collagen type X α1 chain and cyclooxygenase-2 in OA chondrocytes, and enhanced the proliferation of OA chondrocytes, while OA chondrocytes stimulated the production of Col2, sox-9 and aggrecan and promoted hUC-MSCs differentiate into chondrocytes. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated hUC-MSCs have a predominant expression of stem cell markers, while the hematopoietic and endothelial markers were absent. Osteogenic, chondrogenic and adipogenic differentiation was observed in certain induction conditions. hUC-MSCs improved the proliferation of OA chondrocytes and downregulated the expression of inflammatory cytokines, while OA chondrocytes promoted MSCs to differentiate into chondrocytes. Taken together, the co-culture of hUC-MSCs and OA chondrocytes may provide a therapeutic potential in OA treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton’s jelly

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found