- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Comprehensive Investigation of Contrast Sensitivity and Disk Halo in High Myopia Treated With SMILE and EVO Implantable Collamer Lens Implantation
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical outcomes in small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) and EVO implantable Collamer lens (ICL)–treated high myopia.
Methods
Thirty-three SMILE-treated and 32 EVO ICL-treated patients were included and followed up for 6 months. Subjective refraction, contrast sensitivity, and disk halo size were measured preoperatively and postoperatively. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were obtained at the final visit.
Results
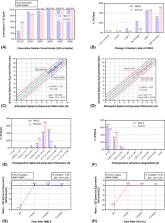
Significant differences in efficacy and safety indices were observed between the SMILE and EVO ICL groups at 6 months postoperatively ( P < 0.05). In the SMILE group, the mesopic contrast sensitivity at 2.2 cycles per degree (cpd) and photopic contrast sensitivity at 0.5, 3.4, and 7.1 cpd were significantly improved. In the EVO ICL group, the mesopic contrast sensitivity at 7.1 cpd and photopic contrast sensitivity at 0.5, 7.1, and 14.6 cpd were significantly improved. The halo radii after SMILE were significantly increased at 1 week, showed a decreasing trend at 1 month, returned to baseline at 3 months, and progressed stably at 6 months. However, it was unchanged in the EVO ICL group. Regarding subjective experience, haloes were the most common disturbance with mild and little bothersomeness after EVO ICL in contrast to starbursts after SMILE.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The development of an instrument to measure quality of vision: the Quality of Vision (QoV) questionnaire.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found