- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Assessment of adolescent and youth friendly services in primary healthcare facilities in two provinces in South Africa
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Health services for adolescents are increasingly recognised as a priority in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The Adolescent and Youth Friendly Service (AYFS) approach has been promoted in South Africa by the National Department of Health and partners, as a means of standardising the quality of adolescent health services in the country. The objective of this paper is to detail the evaluation of AYFS against defined standards to inform initiatives for strengthening these services.
Methods
A cross-sectional assessment of AYFS was carried out in 14 healthcare facilities in a sub-district of Gauteng Province and 16 in a sub-district in North West Province, South Africa. Data on adolescent care and service management systems were collected through interviews with healthcare providers, non-clinical staff and document review. Responses were scored using a tool based on national and World Health Organisation criteria for ten AYFS standards.
Results
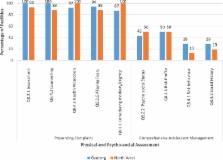
Mean scores for the ten standards showed substantial variation across facilities in the two sub-Districts, with Gauteng Province scoring lower than the North West for 9 standards. The sub-district median for Gauteng was 38% and the North West 48%. In both provinces standards related to the general service delivery, such as Standards 4 and 5, scored above 75%. Assessment of services specifically addressing sexual, reproductive and mental health (Standard 3) showed that almost all these services were scored above 50%. Exploration of services related to psycho-social and physical assessments (Standard 8) demonstrated differences in the healthcare facilities’ management of adolescents’ presenting complaints and their comprehensive management including psycho-social status and risk profile. Additionally, none of the facilities in either sub-district was able to meet the minimum criteria for the five standards required for AYFS recognition.
Conclusion
Facilities had the essential components for general service delivery in place, but adolescent-specific service provision was lacking. AYFS is a government priority, but additional support for facilities is needed to achieve the agreed standards. Meeting these standards could make a major contribution to securing adolescents’ health, especially in preventing unintended pregnancies and HIV as well as improving psycho-social management.
Related collections
Most cited references3
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Does making clinic-based reproductive health services more youth-friendly increase service use by adolescents? Evidence from Lusaka, Zambia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Adolescents' perceptions of health from disadvantaged urban communities: findings from the WAVE study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found