- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Understanding correlates of child stunting in Ethiopia using generalized linear mixed models
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Stunting is an indicator of the devastating result of malnutrition in early childhood. The effects of childhood stunting are irreparable physical and cognitive harm. It is an issue of the great public health importance throughout Sub-Saharan African countries including Ethiopia. Therefore, identification of the risk factors of child stunting from recent data is very important for timely intervention.
Methods
The 2016 Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey data were used for this study. A generalized linear mixed model which is an extension of the general linear model was employed to identify socioeconomic, demographic, environmental and health related risk factors for stunted under-five children.
Results
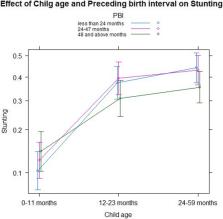
The result shows that the age and sex of the child, preceding birth interval, mother’s body mass index, household wealth index, mother’s education level, breastfeeding period, type of toilet facility, use of internet and source of drinking water were the major determinants of stunting of under-five children in Ethiopia.
Conclusion
The study indicated that children from undernourished mothers, who are not breastfeeding, from poor households, households that have no toilet facilities, who are male, older age (between 12 to 59 months), who have illiterate mother and short birth spacing were associated with stunting problems. Therefore, family planning education and policy is required for the country to improve on under-five age stunting problems.
Related collections
Most cited references11
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long-term consequences of stunting in early life.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found