- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
S100A9 Regulated M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Interleukin-10-Induced Promotion of Malignant Pleural Effusion
Read this article at
Abstract
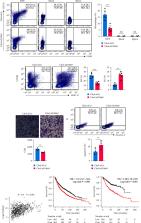
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) promotes the formation and development of malignant pleural effusion (MPE). Previous studies have elucidated the pathogenesis from the view of the immune-regulation function of CD4 + T-cells. However, the underlying mechanism is still not fully understood. In this study, our results showed that IL-10 deficiency reduced the percentage of macrophages in mouse MPE and regulated M1/M2 polarization in vivo and in vitro. The migration capacity of tumor cells was suppressed, and apoptosis was promoted when tumor cells were cocultured with MPE macrophages in the absence of IL-10. Messenger RNA sequencing of MPE macrophages showed that S100A9 was downregulated in IL-10 −/− mice. Bone marrow-derived macrophages obtained from wild-type mice transfected with S100A9-specific small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) also showed less M2 and more M1 polarization than those from the siRNA control group. Furthermore, downregulation of S100A9 using S100A9-specific siRNA suppressed MPE development, decreased macrophages, and modulated macrophage polarization in MPE in vivo. In conclusion, S100A9 plays a vital role in the process of IL-10 deficiency-mediated MPE suppression by regulating M1/M2 polarization, thus influencing the tumor-migration capacity and apoptosis. This could result in clinically applicable strategies to inhibit the formation of MPE by regulating the polarization of MPE macrophages.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Macrophages, innate immunity and cancer: balance, tolerance, and diversity.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found